Motivation or Problems
- There are multiple standards of module system in JS world including CommonJS, AMD, ES6 modules and
<script>tag style. - There are two extremes when transferring modules
- one request per module
- All modules in one request
- Why should a module system only help the developer with JavaScript?
IO
Webpack is a module bundler.
It takes a bunch of files, treating each as a module, figuring out the dependencies between them, and bundle them into static assets that are ready for deployment.
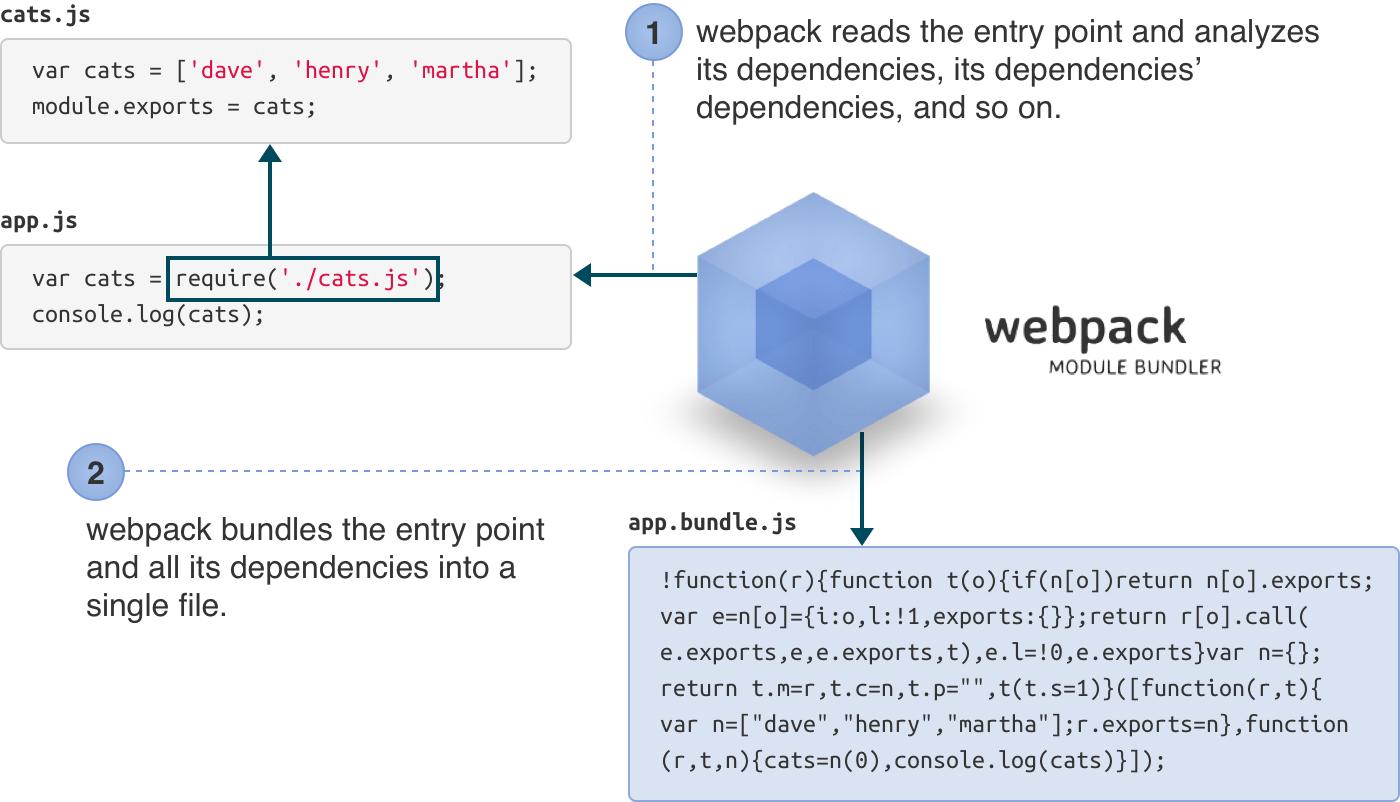
Some concepts of Webpack
chunk: A batch of modules that bundled into one single file.
loader: Transformations that are applied on a resource file(module) of your app.
plugin: Add functionality typically related to bundles in webpack.
Some plugins
DefinePlugin: Allows you to create global constants which can be configured at compile time.
HotModuleReplacementPlugin: Enables Hot Module Replacement.
HtmlWebpackPlugin: Generates a solid base html page for your web application with all your webpack generated css and js files built in.
CommonsChunkPlugin: Generate an extra chunk, which contains common modules shared between entry points.
UglifyJsPlugin: Minimize all JavaScript output of chunks.
ExtractTextPlugin: Extract text from bundle into a file.
Example of Webpack configuration
notice comments start with hash character
{
...
module: {
...
loaders: [
# They are functions that take the source of a resource file as the parameter
# and return the new source.
{ test: /\.less$/,
loader: 'css-loader!less-loader' },
{ test: /\.js$/,
loader: 'babel',
include: '/path-to-your-project/vue-webpack',
exclude: /node_modules/ },
...
]
}
}